For developers, wholesalers, and contractors working across Southeast Asia and Africa, roofing materials must do more than cover a structure—they need to resist high UV exposure, heavy rainfall, coastal salt corrosion, and intense heat. Plastic roofing sheets have become a popular alternative to traditional materials like clay tiles and metal sheets due to their lightweight nature, affordability, and resistance to harsh conditions. But not all plastic roofs perform the same. In this article, we’ll break down five of the most common plastic roofing options used in tropical and coastal regions, helping you understand their core differences, strengths, and ideal applications.
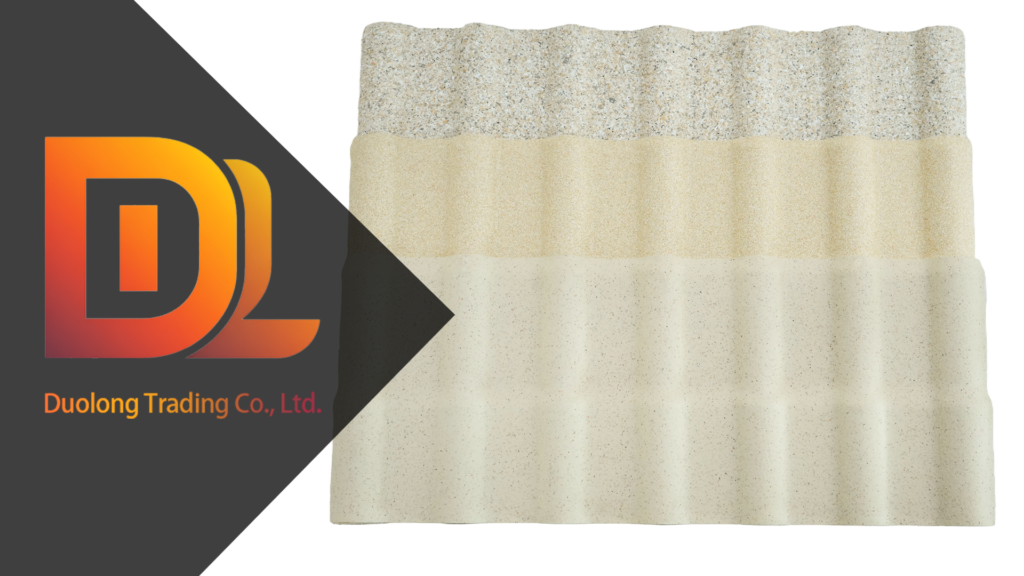
ASA Synthetic Resin Tile: Long-Lasting Color and Tropical Durability
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate) synthetic resin tile is a top-tier roofing solution designed for long-term color retention and extreme weather resistance. Its co-extruded surface layer provides outstanding UV stability and surface gloss, making it ideal for tropical climates with high sun exposure. Unlike traditional tiles, ASA tiles don’t fade, crack, or rust over time, and they’re lightweight enough for fast installation with minimal structural load. This tile is commonly used in villas, schools, government projects, and mid-to-high-end residential buildings.
Key Advantages:
- 10–15 years color stability
- Excellent UV and weather resistance
- No rust, corrosion, or water absorption
- Easy to install and maintain
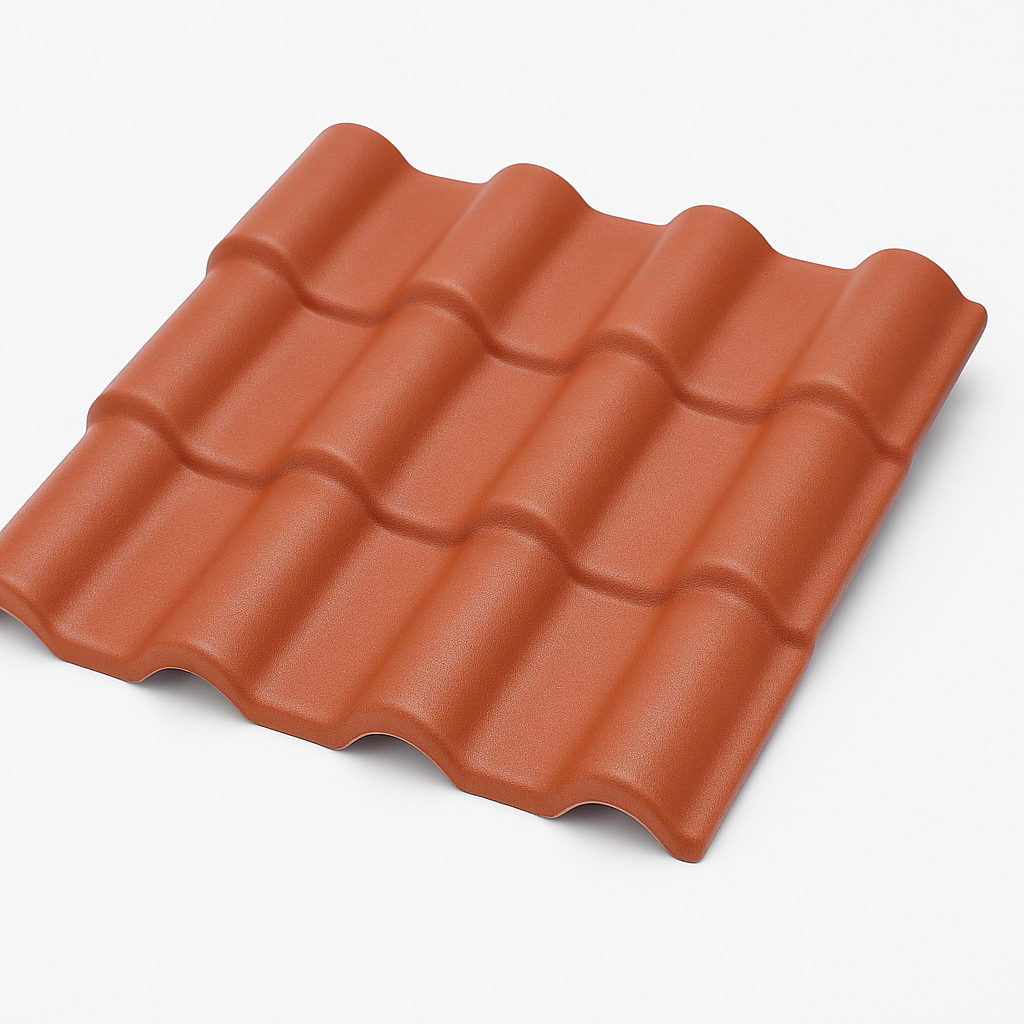

APVC Anti-Corrosion Composite Tile: A Reliable Option for Industrial Roofing
APVC roofing sheets are engineered as a multi-layered composite material designed to resist chemical corrosion, UV damage, and thermal expansion. With an anti-aging surface layer and a reinforced PVC base, this roofing option is especially favored for warehouses, agricultural markets, steel structure workshops, and chemical zones where corrosive gases or salts are present. APVC tiles are more rigid and thicker than basic PVC sheets, providing better insulation, improved load-bearing strength, and longer durability. They are an excellent choice for tropical industrial projects that demand a tough, low-maintenance solution.
Key Advantages:
- Strong resistance to acid, alkali, and salt corrosion
- Higher thickness (often 2.0–3.0mm) enhances durability
- Heat insulation and noise reduction properties
- Ideal for industrial or agricultural roof use
FRP Transparent Roofing Sheet: Cost-Effective Daylighting for Industrial Buildings
FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) transparent roofing sheets are commonly used for natural lighting in large-span structures such as factories, logistics hubs, greenhouses, and animal shelters. These sheets are made by embedding fiberglass into a polyester resin base, offering high light transmittance (60%–85%) while maintaining good mechanical strength. FRP sheets allow daytime sunlight to filter through the roof, reducing electricity costs and improving interior working conditions. They also come in different levels of transparency and thickness depending on specific needs.
Key Advantages:
- High light transmittance with UV protection coating
- Strong impact resistance and structural flexibility
- Lightweight and easy to cut/install
- Commonly used with metal or plastic main roofing systems
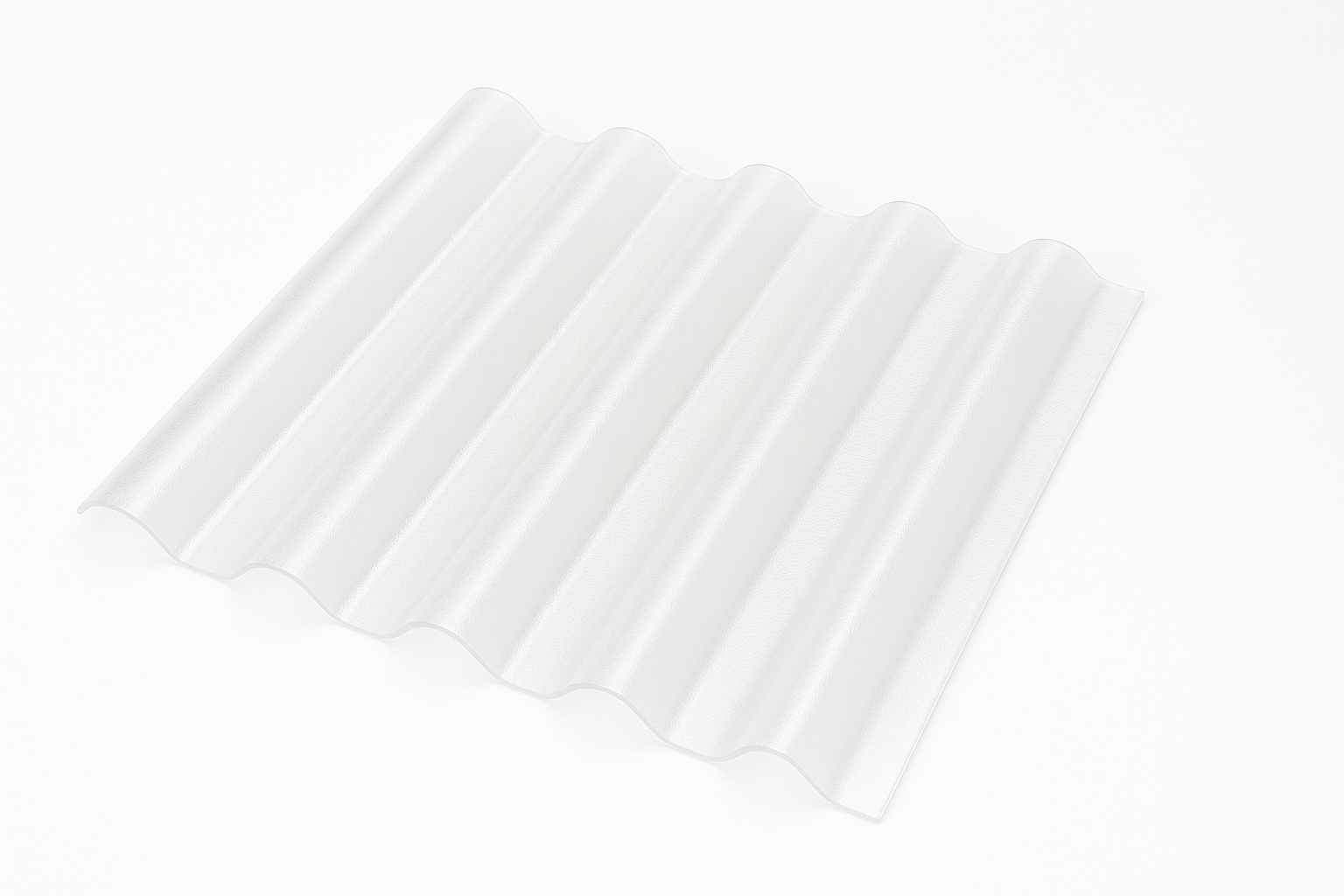

Standard PVC Roof Sheet: Affordable Roofing for Temporary or Low-Budget Projects
Standard PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) roof sheets are a basic and budget-friendly plastic roofing solution used in temporary structures, low-cost warehouses, or simple sheds. Compared to advanced options like ASA or APVC, standard PVC offers lower resistance to UV, corrosion, and thermal expansion. However, for short-term applications or shaded environments, it provides a cost-effective and easy-to-install roofing solution. PVC sheets are often used in small farms, market stalls, and temporary construction sites in regions with milder climates.
Key Advantages:
- Extremely cost-effective
- Lightweight and quick to install
- Suitable for low-load structures or temporary use
- Easy to source and replace
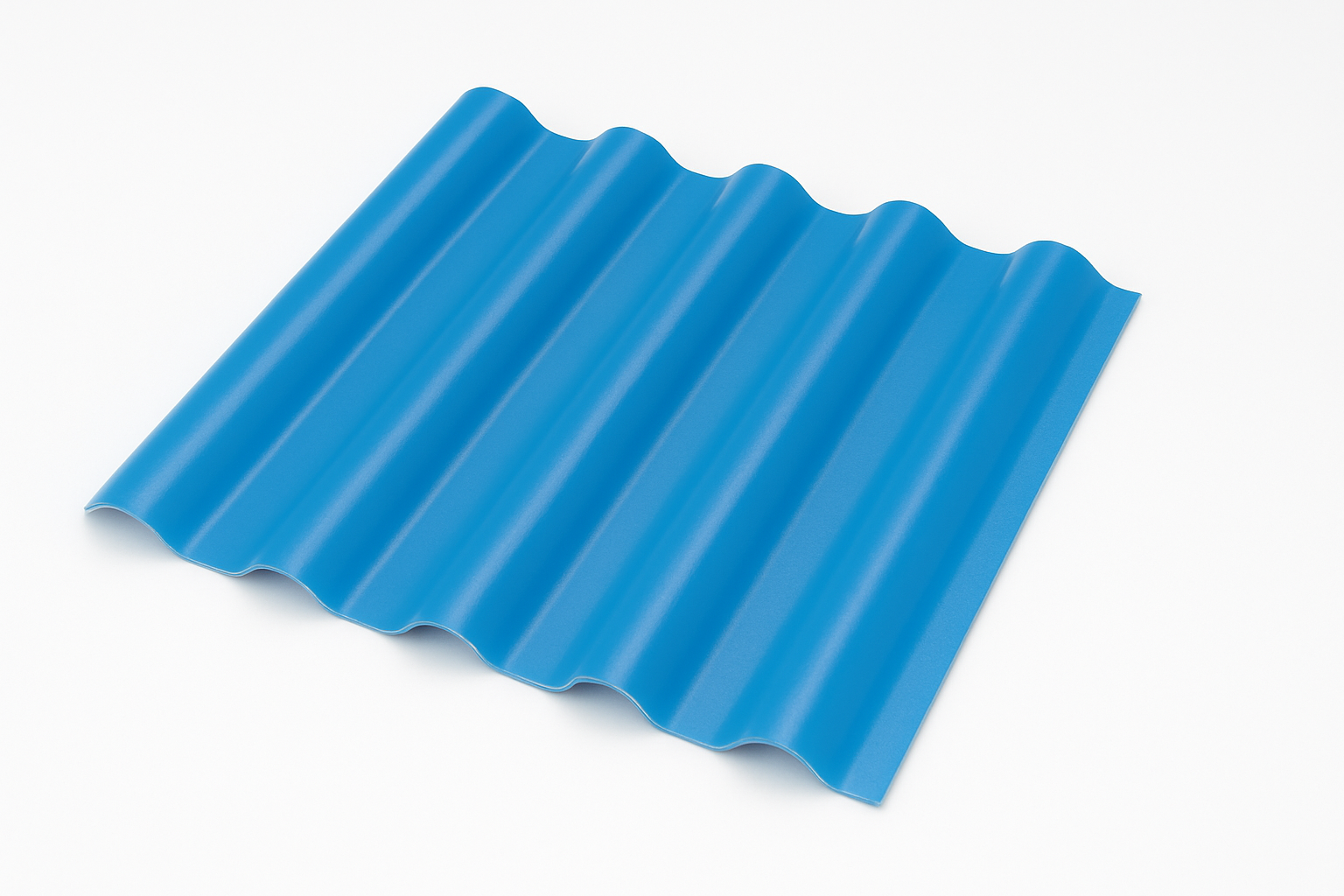

UPVC Multi-layer Roofing Tile: Thermal Insulation and Structural Strength in One
UPVC (Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride) multi-layer roofing tiles are an upgraded form of standard PVC, designed for better heat insulation, sound reduction, and extended service life. These tiles typically consist of two or three layers—an anti-aging UV-resistant surface, a reinforced rigid PVC core, and sometimes a foam or insulation layer in between. This structure improves strength, reduces noise from rain or wind, and helps lower indoor temperatures in hot climates. UPVC roofing is popular for workshops, farms, schools, and low-rise commercial buildings that require comfort and durability without the premium price tag of ASA tiles.
Key Advantages:
- Multi-layer structure enhances insulation and durability
- Lower surface temperature in hot regions
- Reduced noise from rain or external environment
- Cost-effective upgrade from standard PVC
Match Roofing Materials to Project Needs, Not Just Price
In tropical and coastal construction, choosing the right plastic roofing material goes far beyond cost. While standard PVC sheets may suffice for short-term or low-load applications, demanding environments—like seaside factories or urban housing—require more advanced solutions such as ASA tiles or UPVC composites. FRP transparent sheets add value through natural lighting, and APVC offers protection against chemical and salt corrosion. For developers, wholesalers, or contractors, understanding the strengths and limits of each option can directly impact project durability, client satisfaction, and long-term maintenance costs. Always start with your site conditions and functional requirements, and select materials that are built to last.


