In the evolving world of industrial construction, roofing materials are facing new challenges. From chemical exposure in factories to high humidity in markets and harsh UV in outdoor corridors, traditional roofing options—such as metal sheets or asbestos tiles—are showing their age. Corrosion, thermal expansion, noise, and heavy maintenance are common complaints among contractors and building owners alike.
Enter anti-corrosion PVC roofing—a new generation of plastic-based roofing sheets engineered to meet the demands of modern factories, warehouses, and commercial structures. Designed with multi-layer extrusion technology and fortified with UV- and acid-resistant components, these roofing sheets are lightweight, durable, and highly resistant to harsh environments.
As the construction industry shifts toward low-maintenance, high-efficiency, and cost-effective materials, anti-corrosion PVC roofing is gaining popularity across Southeast Asia and Africa. But what exactly is it, and why is it becoming the preferred choice for so many large-scale projects?
This article offers a clear, science-backed explanation of anti-corrosion PVC roofing—what it’s made of, how it works, where it’s used, and how it compares with traditional roofing systems.
What Is Anti-Corrosion PVC Roofing?
Anti-corrosion PVC roofing is a type of plastic-based roofing sheet designed with multi-layer co-extrusion technology. Unlike traditional single-layer plastic or metal roofing, it typically consists of two to three functional layers:
- Top Layer: Made with UV-resistant, anti-aging compounds (sometimes ASA resin) to resist solar degradation and color fading.
- Middle Layer: Reinforced with rigid PVC or calcium-zinc stabilizers to improve structural strength and thermal insulation.
- Bottom Layer: Engineered for chemical resistance and stability in humid or corrosive environments.
This structure allows the sheet to resist acid rain, salt spray, ammonia, industrial fumes, and even long-term exposure to tropical humidity. It’s also lightweight, often weighing 60–70% less than metal sheets, making installation easier and safer for factory and warehouse rooftops.
In global B2B contexts, this material may be referred to as multi-layer PVC roofing sheet, corrosion-resistant plastic roofing, or simply industrial PVC roof panels. “APVC” is the common industry term in Asian manufacturing, though not always recognized by Western buyers.

How It Works: The Science Behind Its Anti-Corrosion Performance
What makes anti-corrosion PVC roofing effective in aggressive environments such as coastal zones, chemical factories, and livestock buildings? The secret lies in its multi-layered polymer structure and chemical additives that protect the material at a molecular level.
- Calcium-zinc stabilizers are added during production to replace toxic lead-based agents, improving resistance to acid rain, ammonia, and high humidity.
- The outer UV-protected layer prevents surface degradation, which often leads to micro-cracks that accelerate chemical corrosion.
- The dense core layer of rigid PVC provides structural integrity and acts as a barrier against chemical penetration.
- In some products, ASA resin or acrylic modifiers further enhance the sheet’s resistance to color fading, weathering, and surface oxidation.
These design choices create a roofing material that withstands long-term exposure to corrosive gases, airborne salts, industrial emissions, and fertilizers—common in warehouses, markets, and coastal factories.
Unlike metal roofing, which is prone to rust, or fiber cement tiles that degrade over time, anti-corrosion PVC sheets maintain their integrity and appearance with minimal maintenance. This makes them an ideal solution for humid, corrosive, or poorly ventilated environments.
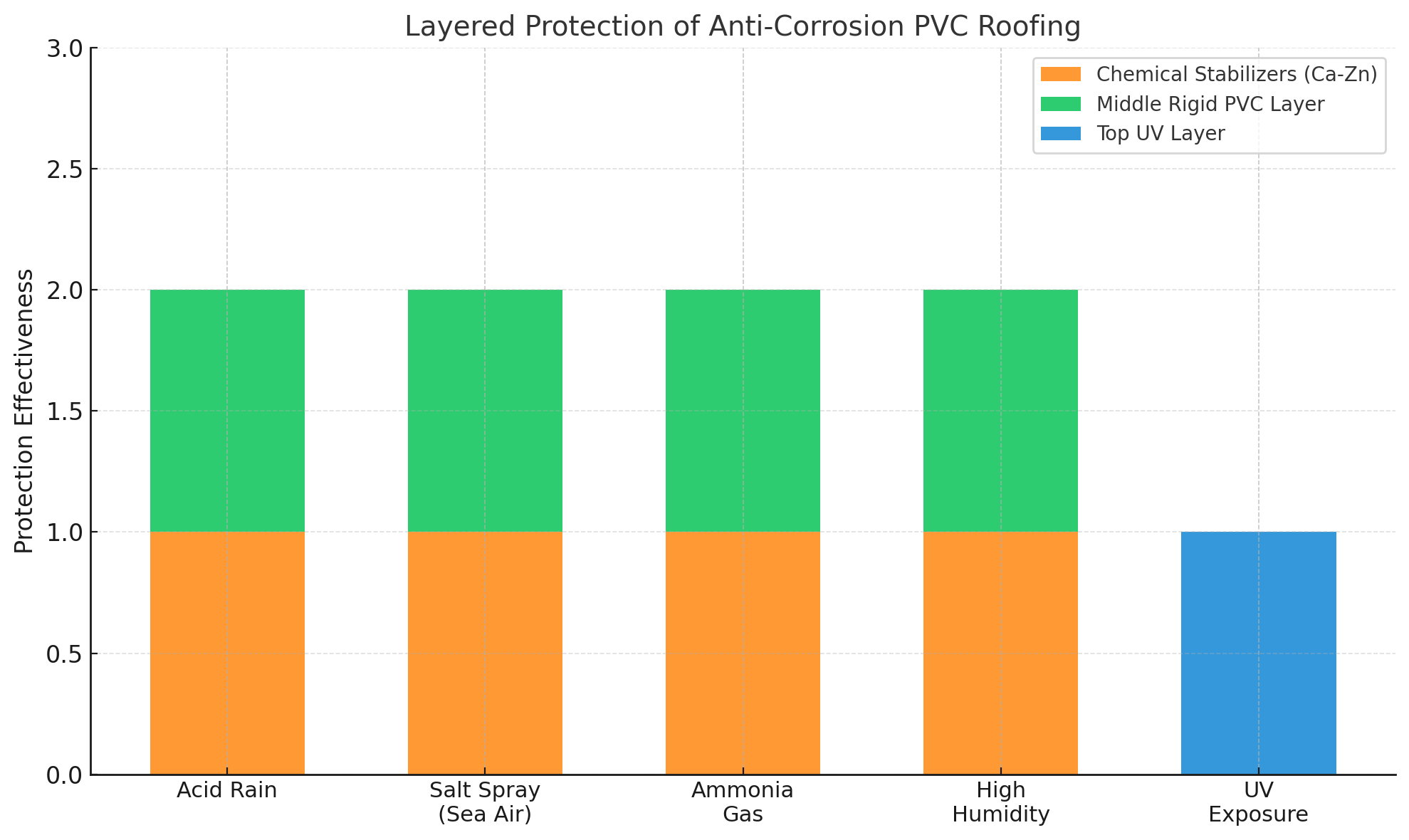
The chart above illustrates how the three functional layers of anti-corrosion PVC roofing—UV-protected top layer, rigid PVC core, and calcium-zinc stabilizers—each serve a distinct purpose in resisting different environmental threats.
- UV Exposure is primarily handled by the top UV-resistant layer, which shields the surface from degradation and color fading.
- Acid rain, salt spray, ammonia gas, and high humidity are mitigated through the core PVC structure and chemical stabilizers, ensuring long-term structural integrity.
This layered defense mechanism explains why these roofing sheets are widely used in coastal, chemical, and agricultural environments where conventional roofing quickly fails.
Real-World Applications: Where Is It Most Commonly Used?
Anti-corrosion PVC roofing is engineered for environments where durability, chemical resistance, and long-term stability are essential. Its versatility allows it to be deployed across a wide spectrum of industrial and commercial buildings, particularly in developing regions with tropical or coastal climates.
Here are some of the most common application scenarios:
- Steel Structure Factories: In modern manufacturing plants, APVC roofing is used to cover large-span steel structures, offering corrosion protection against moisture, chemicals, and exhaust gases without the noise issues of metal roofing.
- Wholesale Markets and Trading Corridors: These public-use spaces often experience high foot traffic, humidity, and temperature swings. APVC provides shade, rain protection, and reduces heat transfer, making it ideal for covered walkways and vendor areas.
- Logistics Warehouses and Distribution Centers: Warehouses benefit from APVC’s low thermal conductivity and low maintenance needs, which help stabilize internal temperatures and reduce operational costs.
- Agricultural Processing Zones: In facilities like feed mills or fertilizer storage, APVC sheets withstand ammonia and acidic gases far better than traditional materials.
- Vehicle Shelters and Parking Sheds: Due to its lightweight and noise-reducing properties, APVC is a great fit for roofing carports and sheds in both commercial and residential settings.
Whether it’s a coastal industrial park or a bustling city-side warehouse, APVC roofing has proven itself as a smart, sustainable material choice that adapts to modern construction needs.

Why Choose It Over Metal or Asbestos Alternatives?
When selecting a roofing material for industrial or commercial use, many buyers still consider metal sheets or asbestos tiles due to their familiarity or low upfront cost. However, these materials often come with long-term drawbacks in today’s construction environments.
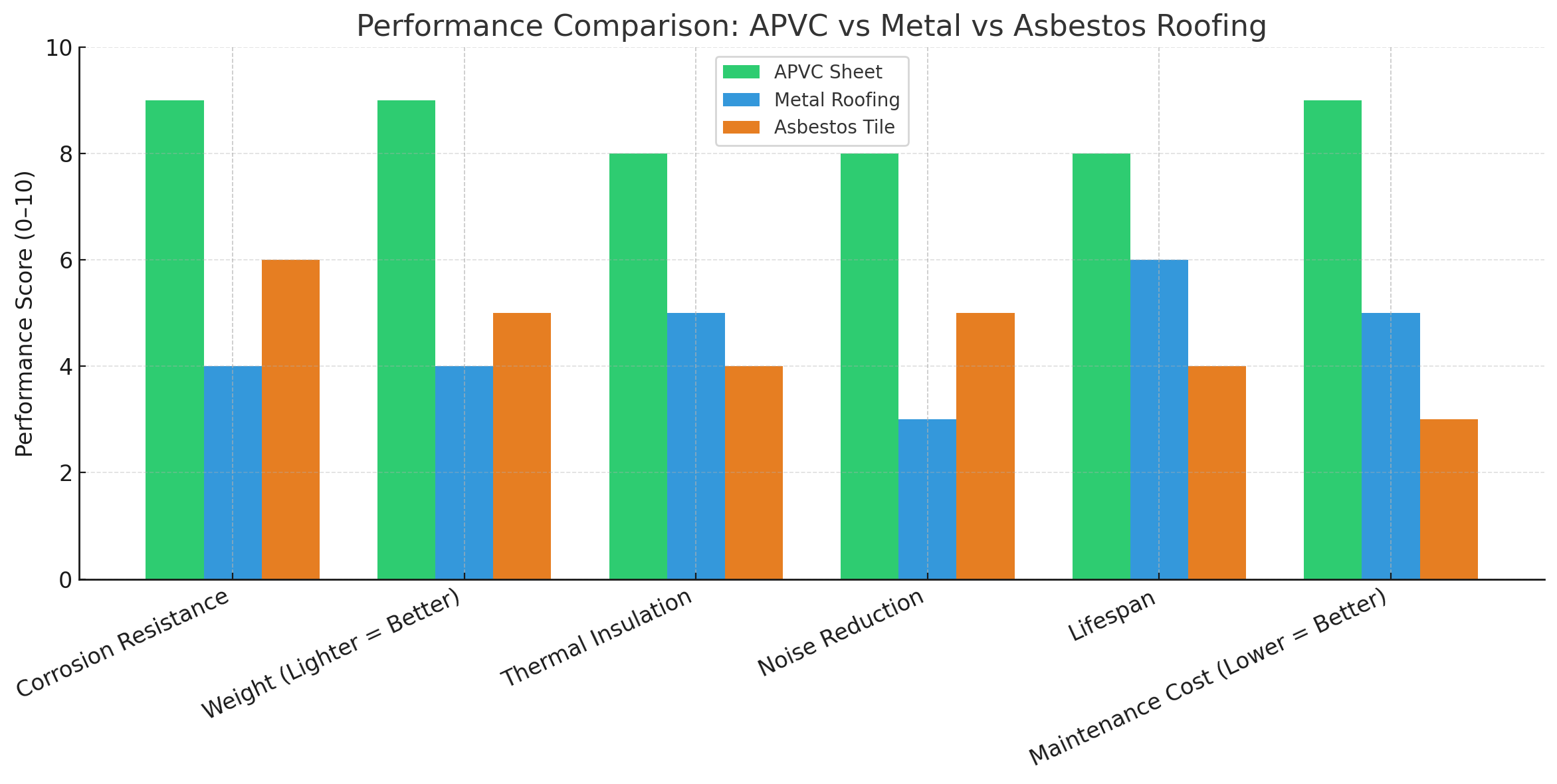
Here’s how anti-corrosion PVC roofing compares:
- Corrosion Resistance Unlike metal roofing, which is highly vulnerable to rust, salt spray, and acidic fumes, APVC roofing resists chemical attack without any painting or surface treatment.
- Weight and Structural Load APVC sheets weigh significantly less than metal or asbestos, reducing structural stress and making it easier to transport and install, especially in large-span steel structures or temporary constructions.
- Thermal and Acoustic Insulation APVC offers better insulation against both heat and noise, helping lower internal temperatures and creating quieter environments—important for markets, warehouses, and workshops.
- Maintenance and Lifespan Metal roofing may require regular repainting or sealing. Asbestos tiles degrade over time and carry health risks. In contrast, APVC requires minimal upkeep and remains stable for 15–25 years, depending on conditions.
- Environmental and Safety Considerations Asbestos has been banned or restricted in many countries due to its health risks. APVC is a lead-free, recyclable material, aligning with modern standards for safe, eco-friendly construction.
While metal and asbestos roofs had their place in the past, anti-corrosion PVC roofing delivers a smarter, longer-lasting solution for the demands of today’s projects.
Buying Tips: What to Check Before Choosing APVC Roofing
While anti-corrosion PVC roofing offers strong technical advantages, not all APVC sheets are created equal. Variations in formulation, production technology, and quality control can result in significantly different product performance.
Before making a purchase, B2B buyers should consider the following:
- Check the Layer Structure High-quality APVC roofing is typically a three-layer co-extruded product, with a UV-resistant surface layer, a rigid PVC core, and stabilizers. Ask for a cross-sectional sample or third-party test report.
- Verify Raw Material Sources The use of virgin, non-recycled PVC and Ca-Zn stabilizers ensures better corrosion resistance and safety. Be cautious of overly cheap sheets, which may contain recycled or heavy-metal additives.
- Understand the Thickness Range Different applications require different thicknesses. For large-span industrial buildings, sheets between 2.0mm–3.0mm are recommended to ensure mechanical strength and wind resistance.
- Request Fire-Retardant Certifications In commercial settings, especially warehouses or markets, fire performance is critical. Look for APVC sheets rated as Class B1 or above in flame retardancy.
- Ensure Manufacturer Reputation & Experience Choose a supplier with stable export experience, factory-level production control, and technical support. Long-term usage relies not just on product quality, but also on post-sale assistance and delivery efficiency.
Ultimately, good APVC roofing is not about price alone—but a balance of formulation, certification, and service.
Build Smarter, Last Longer: Why APVC Is More Than Just a Roof
From its multilayer anti-corrosion structure to its long-term durability, recyclable formulation, and cost-effectiveness, anti-corrosion PVC roofing (commonly known as APVC) is no longer a niche product—it’s becoming a preferred roofing solution for industrial and commercial projects across emerging markets.
Whether you’re building a logistics warehouse in Africa, upgrading a steel structure factory in Southeast Asia, or seeking a low-maintenance roof for public market corridors, APVC roofing offers a rare balance of performance, safety, and sustainability.
At Duolong, we specialize in the manufacture and export of high-quality APVC roofing sheets with full customization options, export documentation, and technical support. We work with construction contractors, distributors, and importers across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
Contact us today to get free samples, request detailed specs, or discuss your wholesale needs. Let’s build better, longer-lasting roofs—together.


